The advent of 5G technology marks a watershed moment in the evolution of wireless communication. Unlike the incremental improvements seen in previous generations, 5G represents a fundamental redesign of network architecture and capabilities. Understanding the depth and breadth of this technology is crucial for businesses, technologists, and consumers alike as we enter an era of unprecedented connectivity.
Through our comprehensive exploration of 5G technology, you’ll understand how it’s becoming the backbone of our increasingly connected world and why experts predict it will generate $1.3 trillion in business value by 2028.
Table of Contents
ToggleThe Foundation of 5G Technology
Technical Revolution
At its core, 5G is built on three fundamental pillars that distinguish it from previous generations:
Enhanced Mobile Broadband (eMBB)
- Peak data rates reaching 20 Gbps
- Sustained high speeds in dense urban environments
- Revolutionary applications in “AR/VR Applications Powered by 5G”
Ultra-Reliable Low-Latency Communications (URLLC)
- Latency as low as 1 millisecond
- 99.999% reliability for critical applications
- Enabling “Connected Vehicles and V2X Communication”
Massive Machine-Type Communications (mMTC)
- Support for up to 1 million devices per square kilometer
- Powering the future of “Industrial IoT and 5G Manufacturing”
Network Architecture Deep Dive
Revolutionary Design Philosophy
The architecture of 5G networks represents a complete departure from traditional cellular networks. Our detailed analysis in Understanding 5G Network Architecture reveals how the network is built on a service-based architecture (SBA) that enables unprecedented flexibility and scalability.
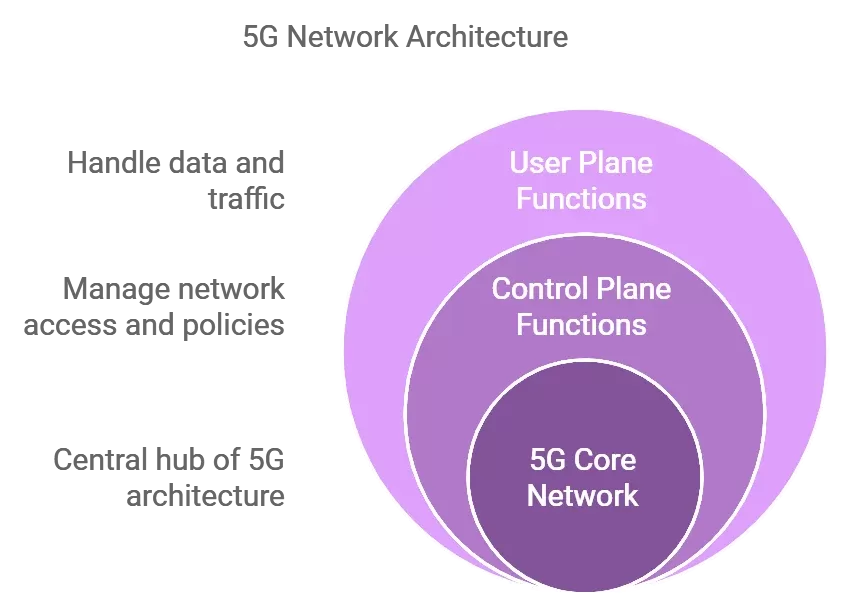
Core Network Components
The 5G core network (5GC) utilizes a revolutionary cloud-native approach:
Control Plane Functions:
- Access and Mobility Management Function (AMF)
- Session Management Function (SMF)
- Policy Control Function (PCF) As detailed in our “5G Infrastructure Components: A Complete Guide”
User Plane Functions:
- Data forwarding
- QoS handling
- Traffic measurement Learn more in “5G Base Station Technology”
Spectrum Innovation
Multi-Band Approach
5G’s spectrum utilization represents a major leap forward, as explored in our “5G Spectrum Explained: mmWave vs. Sub-6” analysis:
Low-Band (Sub-1 GHz)
- Coverage: Up to 10 km
- Speed: 30-250 Mbps
- Use cases: Rural coverage, IoT
Mid-Band (1-6 GHz)
- Coverage: 1-3 km
- Speed: 100-900 Mbps
- Use cases: Urban and suburban coverage
High-Band (mmWave, 24 GHz+)
- Coverage: < 500 meters
- Speed: 1-20 Gbps
- Use cases: Dense urban areas, venues
Revolutionary Features
Network Slicing
Network slicing, detailed in “Network Slicing in 5G: How it Works”, enables operators to create multiple virtual networks over a single physical infrastructure. This groundbreaking capability allows:
- Customized network characteristics for specific applications
- Dynamic resource allocation
- Guaranteed quality of service (QoS)
- Isolation between different services
Advanced MIMO Technology
Massive MIMO, explored in “Massive MIMO and Beamforming Technology”, revolutionizes wireless communication through:
- Hundreds of antenna elements
- Advanced beamforming techniques
- Spatial multiplexing
- Improved spectrum efficiency

Industry Transformations
Healthcare Revolution
5G is fundamentally transforming healthcare delivery, as detailed in “5G in Healthcare: Transforming Patient Care”:
Remote Surgery
- Ultra-low latency: < 1ms
- Haptic feedback
- Real-time HD video streaming
- Robotic control precision
Advanced Diagnostics
- Real-time image processing
- AI-powered diagnosis
- Remote patient monitoring
- Emergency response optimization
Manufacturing Evolution
The impact on manufacturing, covered in “Industrial IoT and 5G Manufacturing”, includes:
Smart Factory Applications
- Real-time production monitoring
- Predictive maintenance
- Digital twins
- Autonomous systems
Quality Control
- AI-powered visual inspection
- Real-time defect detection
- Production line optimization
- Supply chain integration
Security Framework
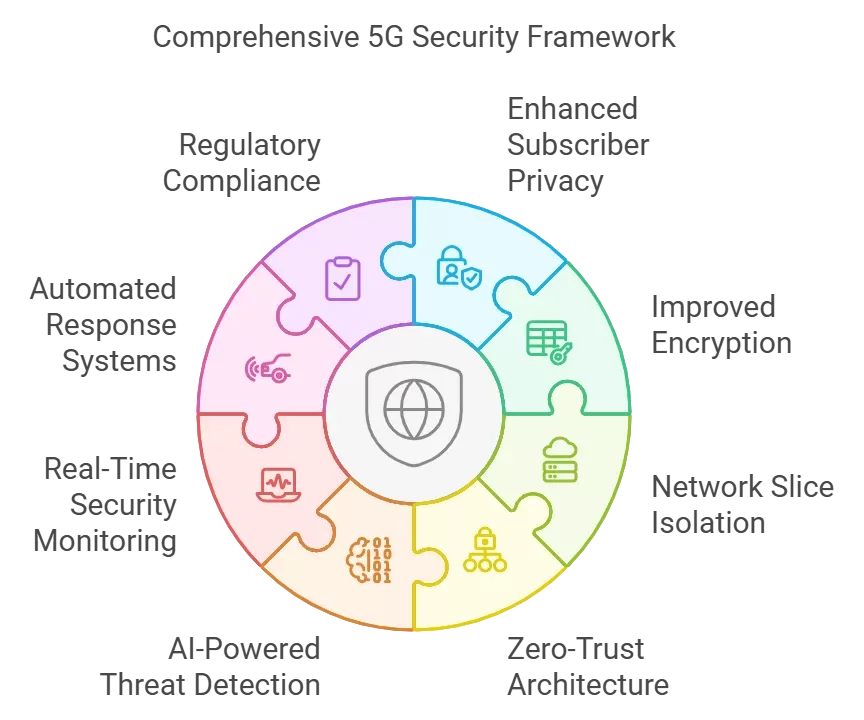
Enhanced Security Architecture
Security in 5G, detailed in “5G Network Security Architecture”, introduces:
Advanced Security Features
- Enhanced subscriber privacy
- Improved encryption
- Network slice isolation
- Zero-trust architecture
Threat Protection
- AI-powered threat detection
- Real-time security monitoring
- Automated response systems
- Regulatory compliance
Economic Impact
Market Transformation
The economic implications of 5G, analyzed in “Economic Impact of 5G Technology”, show:
Market Growth
- Global market value: $797.8B by 2030
- Job creation: 22.8M new jobs by 2025
- Industry investment: $1.1T through 2025
- GDP impact: $2.2T by 2034
Industry Vertical Impact
- Manufacturing: $740B impact
- Public services: $985B impact
- Healthcare: $530B impact
- Retail: $1.2T impact
Future Horizons
Beyond 5G
The evolution continues, as explored in “6G Technology: What’s Next?”, with:
6G Development
- Terahertz frequencies
- Holographic communications
- Quantum networking
- AI integration
Enhanced Capabilities
- Sub-0.1ms latency
- 1 Tbps peak data rates
- Spatial internet
- Brain-computer interfaces
Conclusion
5G technology represents more than just an improvement in wireless communication—it’s a fundamental shift in how we connect, work, and live. As deployment continues globally, its transformative impact will only grow, enabling innovations we’re just beginning to imagine.
Expert Insights
“5G is not just about faster phones. It’s about connecting everything around us in ways that were previously impossible.” – Dr. Sarah Chen, Telecommunications Expert






