When building or upgrading your PC, motherboard prices can shock you – ranging from just $100 to over $1000 for premium models. Why such a huge gap? It’s not just about features. Many factors determine costs. Choosing the right motherboard can be confusing when price is the priority. But most expensive doesn’t always mean best quality. Let’s unpack what’s driving premium motherboard costs so high. From advanced R&D to complex manufacturing to product positioning, premium engineering and technology come at a premium price. Read on to appreciate why quality has its price.
The key points covered:
🌟 Large price range for motherboards
🌟 Many factors beyond features determine costs
🌟 Confusing to choose just based on price
🌟 Expensive doesn’t necessarily mean best
🌟 Goal is explaining high costs of premium motherboards
🌟 Factors like R&D, manufacturing, positioning
🌟 Quality engineering and tech is expensive
Table of Contents
ToggleAdvanced Components Carry Premium
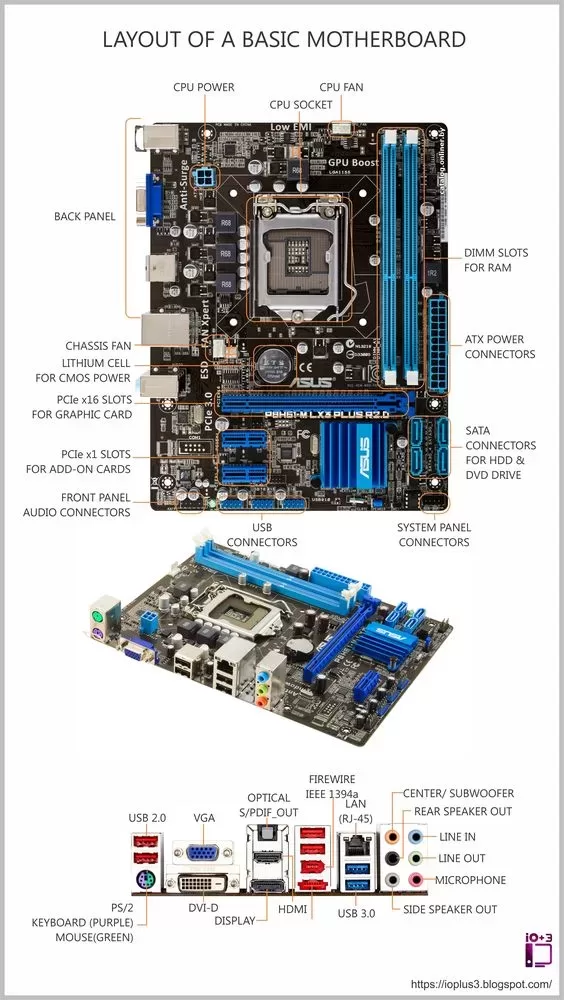
Cutting Edge CPUs and Chipsets
Only the fastest, most sophisticated current generation CPUs and chipsets find their way onto premium boards. Flagship offerings like blistering Intel Core i9s with 10+ cores and unlocked AMD Ryzen Threadripper PROs with stratospheric core counts supply otherworldly throughput but accompany equally astronomical price tags thanks to their intricately engineered designs and nimble process nodes.
Extreme Memory and Storage Support
Supporting outrageous amounts of lighting fast DDR4 or upcoming DDR5 RAM running at extreme clocks enables unmatched responsiveness but mandates intricate PCB engineering and leading-edge memory slot technology to extract every last drop of bandwidth. Multiple Direct Lanes for NVMe PCIe solid state drives provide massive throughput for content creation tasks but require extra interconnects and controllers.
Next-Generation I/O and Power Delivery
Myriad USB, SATA, Ethernet, and WiFi standards provide seamless ecosystem connectivity and ensure readiness for tomorrow’s peripherals but each carries licensing and integration costs. Even intricate power regulation and delivery components sculpted to deliver absurd wattage totals with rock steady voltage rails contribute to the premium price point.
Substantial R&D Investments
Rigorous Compatibility Validation
Meticulous design rigor including extensive simulation of electrical performance and thermal conditions combines with exhaustive physical validation across a nearly limitless array of CPU, memory, add-in cards and other configurations to guarantee stability and reliability. But the sheer engineering and testing time racks up costs rapidly.
Continuous Standards Adoption
With bleeding edge standards like DDR5 memory, PCIe 5.0, and next-gen USB emerging constantly, manufacturers invest heavily in navigating the logistical maze of rapid, early adoption to deliver future-looking boards while ensuring seamless integration. Such efforts require extensive R&D budgets.
Cost Breakdown
Here is an example cost breakdown for a high-end motherboard:
- PCB Fabrication and Assembly – 30%
This includes the bare PCB fabrication using advanced multilayer processes as well as SMT assembly and testing of all components. High complexity results in higher costs.
- Components – 45%
CPU, memory, slots, controllers etc. make up nearly half the total BOM. High-end versions of these carry premiums.
- R&D Investments – 15%
Extensive engineering, validation testing, standards adoption, and feature development add significantly to the overhead.
- Marketing, Logistics – 5%
Branding, distribution, retail margins make up the remainder of costs. High-end boards emphasize premier support experiences.
- Profit Margins – 5%
While overhead costs are substantial, profit margins tend to remain modest on high-end boards. Competition is fierce at the top end.
In summary, advanced component selections, manufacturing complexity, and continuous R&D requirements make up the majority of costs. But ancillary expenses like distribution and branding also factor in. At high pricing tiers, margins remain tighter as competition is intense. Let me know if you would like me to modify the percentage breakdown or add any additional commentary!
👉 Learn more about the Motherboards Cracks:
-
- Cracking the Motherboard Yellow Light – Yellow Light on Motherboards, Causes and Tips & Tricks. 🚀
- SATA Port Motherboards – Ultimate Guide in 2025. 💻
Don’t miss these awesome blog posts. 😊
Premium Trends
New technologies driving costs up:
- PCIe 5.0 – Adopting the latest PCIe standard requires revised PCB layouts, better signal integrity practices, and PCIe 5.0 controllers which are currently more expensive.
- DDR5 memory – The jump to DDR5 RAM necessitates revised memory slot designs and PCB stackups to handle the increased speeds. Initial DDR5 pricing is also higher.
- Faster USB standards – Moving to USB 3.2, USB4 and upcoming USB standards requires integrating new generation PHYs and controllers before economies of scale kick in.
- Higher layer count boards – Increasing layer counts to accommodate faster signaling further drives fabrication costs.
- Advanced power design – More phases, better thermal management and transient response requires high-end components.
Economies of scale reducing costs:
- CPUs – As adoption ramps of new high-core count CPUs, costs decline over time.
- Framework maturation – After initial rollouts, subsequent revisions benefit from debugged designs.
- Test optimization – Re-using validation frameworks, automation and test benches improves efficiency.
- Manufacturing yields – As fabrication lines mature, yield rates improve resulting in lower per unit costs.
So in summary, rapid technology iterations are driving costs upward but over 12-24 month timeframes improved economies of scale partially offset the introductions of next-gen platforms.
Final Thoughts
High-end motherboards justify steep price tags through elite components, substantial engineering rigor, and advanced manufacturing techniques enabling uncompromising top-tier performance. Cutting-edge Multi-Core CPUs, vast fast memory support, next-generation I/O, and robust power delivery carry premiums but provide record-breaking speed. Extensive validation testing ensures flawless stability. Exotic PCB materials and processes add costs but are necessary for extreme capability. While prohibitive to budget builders, devoted enthusiasts recognize the value gained in peerless computing power, smooth expandability, and unyielding quality when paying more. For utmost capability, premium pricing grants access to the bleeding edge.
FAQs
Cutting-edge multi-core CPUs, abundant fast memory support, next-generation I/O controllers, exotic PCB materials, and low initial manufacturing yields primarily contribute to high costs.
For enthusiasts seeking uncompromising top-tier speed, quality, and capability, the costs are justified. But budget-focused builders may find better value with more affordable options.
Higher-end boards enable CPU/memory overclocking, increased core counts, abundant fast storage, unrestricted power delivery, and bandwidth for add-in cards.
Choosing last-gen instead of brand new components, minimizing extra features, and shopping sales/open box deals can lower total outlay.